How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying. This guide provides a step-by-step approach, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced maneuvers and legal considerations. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone flight, equipping you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
Mastering drone operation requires understanding its mechanics, navigation, and legal implications. We’ll delve into each aspect, providing clear explanations and practical tips to ensure your flights are not only successful but also safe and compliant with regulations. From selecting the right flight mode to understanding airspace restrictions, this guide serves as your comprehensive handbook for safe and responsible drone piloting.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures: How To Operate A Drone
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting key components, verifying system functionality, and understanding potential risks. Ignoring these steps can lead to accidents, equipment damage, or even injury.
Pre-flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection involves several key steps to ensure your drone is in optimal condition. This includes checking the battery level, inspecting the propellers for damage, and verifying a strong GPS signal.
| Step | Purpose | Potential Consequence | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Check | Ensure sufficient power for the planned flight duration. | Unexpected power loss mid-flight, leading to a crash. | Check battery level indicator and ensure it’s adequately charged. Consider carrying a spare battery. |
| Propeller Inspection | Identify any damage or wear that could affect flight stability. | Unbalanced propellers can cause vibrations, instability, and crashes. | Visually inspect each propeller for cracks, bends, or other damage. Replace damaged propellers. |
| GPS Signal Strength Verification | Ensure accurate positioning and stable flight control. | Loss of GPS signal can lead to erratic flight behavior and loss of control. | Check the GPS indicator on your controller and ensure it shows a strong signal before takeoff. Avoid flying in areas with poor GPS reception. |
| Gimbal and Camera Check | Ensure the camera is properly mounted and functioning correctly. | Poor image quality or camera malfunction. | Power on the camera and check for image clarity and functionality. |
Safe Launch and Landing Procedures
Launching and landing a drone safely requires a methodical approach. This ensures the drone takes off and lands smoothly, minimizing the risk of damage or accidents.
- Find a clear, open area free from obstacles.
- Ensure the propellers are clear of any obstructions.
- Calibrate the compass and GPS if necessary.
- Slowly increase throttle to initiate ascent.
- For landing, gradually decrease throttle until the drone gently touches down.
- Power off the drone after landing.
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergencies is vital for safe drone operation. This includes addressing situations such as loss of signal and low battery warnings.
- Loss of Signal: Most drones have a “Return to Home” (RTH) function. Activate this immediately if you lose signal. If RTH fails, try to manually maneuver the drone back to your location based on your last known position.
- Low Battery: Land the drone immediately upon receiving a low battery warning. Never attempt to push the drone’s limits by flying until it completely shuts down.
Drone Controls and Operation
Understanding the basic controls of your drone is essential for safe and effective operation. This includes mastering throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll, as well as understanding different flight modes.
Basic Drone Controls
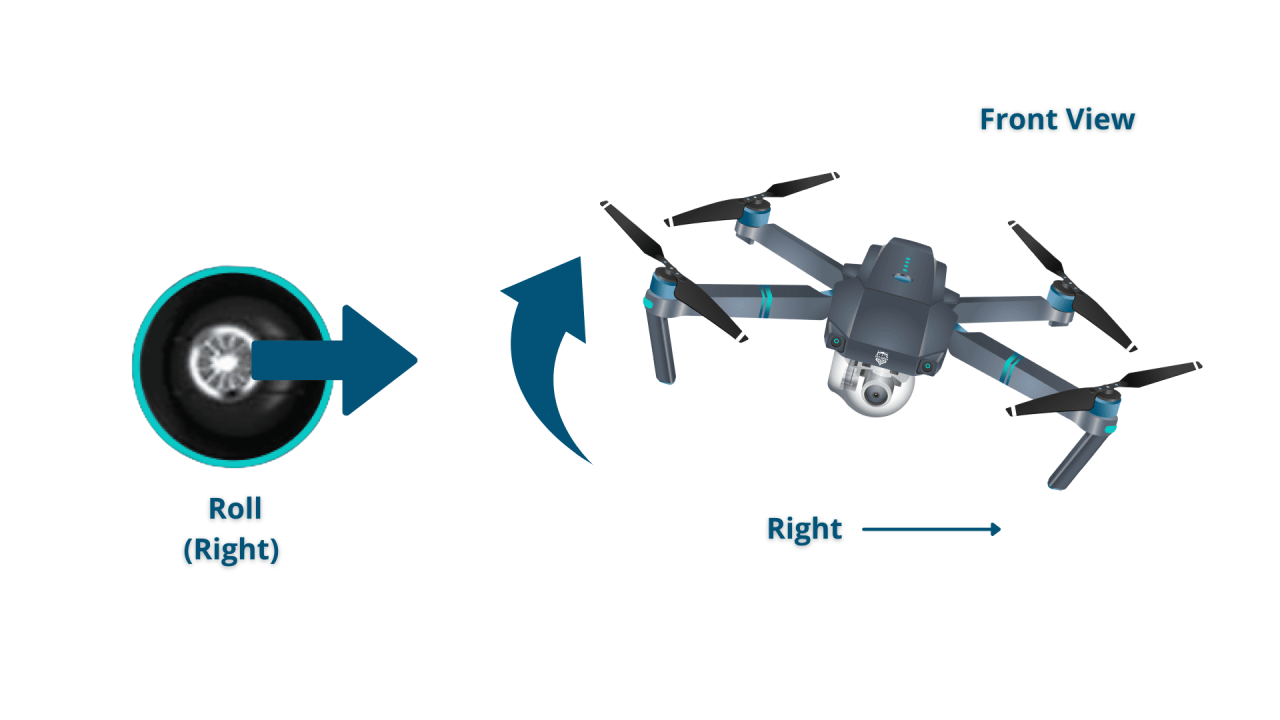
Standard drone controls typically involve four primary axes: throttle (altitude control), yaw (rotation around the vertical axis), pitch (forward/backward tilt), and roll (left/right tilt). Most controllers use joysticks or similar input devices to manage these controls. Understanding the relationship between these controls is key to precise maneuvering.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes cater to varying skill levels and flight situations. Beginner mode typically limits speed and responsiveness, enhancing stability. Sport mode unlocks higher speeds and increased responsiveness, suitable for experienced pilots.
Precise Maneuvering and Hovering
Precise maneuvering and stable hovering require practice and a delicate touch on the controls. Small, controlled adjustments are key to maintaining position and avoiding erratic movements.
Basic Aerial Maneuvers
Mastering basic aerial maneuvers such as ascents, descents, turns, and lateral movements forms the foundation for more advanced flight techniques. Practice these movements in a safe and open area to develop proficiency.
Flight Planning and Navigation
Safe and efficient flight planning is crucial for avoiding accidents and ensuring successful drone missions. This includes identifying potential hazards, selecting appropriate flight paths, and understanding airspace regulations.
Safe Flight Path Strategies
Plan your flight path carefully, considering potential obstacles like buildings, trees, power lines, and people. Maintain a safe distance from these hazards, and always keep your drone within visual line of sight (VLOS) unless operating under specific exemptions.
Potential Hazards
Identify and avoid potential hazards such as restricted airspace (airports, military zones), crowded areas, and areas with poor GPS signal. Check local regulations before flying.
Sample Flight Plan
Consider a scenario of aerial photography of a building. A sample flight plan could involve the following waypoints:
- Waypoint 1: Takeoff and ascend to 50 feet.
- Waypoint 2: Move laterally to position the building centrally in the frame.
- Waypoint 3: Orbit the building at a constant distance, capturing photos from various angles.
- Waypoint 4: Descend to 10 feet and move to a safe landing zone.
- Waypoint 5: Land the drone.
GPS and Waypoints for Autonomous Flight
Many drones offer autonomous flight capabilities using GPS and pre-programmed waypoints. This allows for pre-planned flights with minimal manual control, ideal for tasks like aerial surveys or inspections.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings, composition techniques, and post-processing workflows.
Tips for High-Quality Aerial Media
Use a high-resolution camera, ensure proper lighting, and experiment with different angles and perspectives to capture compelling visuals. Consider using filters to enhance image quality.
Importance of Lighting and Composition
Good lighting is crucial for high-quality photos and videos. Avoid harsh shadows by shooting during the golden hours (sunrise and sunset) or using appropriate lighting equipment. Composition is equally important, utilizing the rule of thirds and leading lines to create visually appealing shots.
Setting up and Using a Drone Camera
Familiarize yourself with your drone’s camera settings, including ISO, shutter speed, and aperture. Experiment with different settings to achieve the desired look and feel for your photos and videos.
Transferring and Editing Drone Footage, How to operate a drone
Transfer your footage from the drone’s SD card to your computer using a card reader. Use video editing software to enhance your footage, adding effects, transitions, and music.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the complexities requires a good grasp of safety protocols and airspace regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all these areas, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone which offers step-by-step instructions and helpful tips. Ultimately, responsible drone operation ensures both safety and enjoyable flight experiences.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are essential for prolonging the lifespan of your drone and preventing unexpected issues during operation.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance includes cleaning, inspecting, and lubricating moving parts. This helps prevent wear and tear, ensuring the drone functions optimally.
Post-Flight Cleaning and Inspection
After each flight, carefully clean the drone’s body, propellers, and camera lens. Inspect for any damage and address any issues immediately.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Drone won’t power on | Check battery level, ensure proper connections, and try a different battery. |
| Poor GPS signal | Relocate to an area with better GPS reception. |
| Erratic flight behavior | Calibrate the compass and GPS, check for propeller damage. |
| Low battery warning | Land the drone immediately and recharge the battery. |
Replacing Damaged Parts
If a part is damaged, replace it with an original or compatible part to maintain optimal performance. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for part replacement.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance

Operating a drone responsibly requires adherence to local laws and regulations. Understanding these rules is crucial to avoid penalties and ensure safe operation.
Relevant Laws and Regulations
Familiarize yourself with the specific laws and regulations governing drone operation in your area. These regulations often cover registration requirements, flight restrictions, and operational guidelines.
Permits and Licenses
Depending on your location and intended use, you may need to obtain permits or licenses before operating a drone. Check with your local aviation authority for specific requirements.
Drone Registration

Register your drone with the appropriate authorities as required by law. This ensures your drone is properly identified and helps track its operation.
Restricted Areas
Avoid flying your drone in restricted areas, such as airports, military bases, and national parks. Always check for no-fly zones before launching your drone.
Advanced Drone Techniques
Advanced drone techniques enable the creation of cinematic shots and complex maneuvers, requiring a high level of skill and practice.
Cinematic Drone Shots
Cinematic drone shots involve creative camera movements and angles to enhance storytelling and visual appeal. This includes techniques like orbiting, tracking shots, and smooth transitions.
Achieving Specific Camera Movements
Mastering camera movements like orbiting (circling a subject), tracking shots (following a moving subject), and smooth ascents and descents requires practice and precise control of the drone’s movements.
Advanced Features
Utilize advanced features such as obstacle avoidance and return-to-home (RTH) functionality to enhance safety and efficiency. These features help mitigate risks and ensure safe operation.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, from pre-flight checks to maneuvering, is crucial for safe and effective operation. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from takeoff to landing, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone before your first flight. Mastering the art of drone operation takes practice and patience, but the results are well worth the effort.
Comparing Drone Models
Different drone models offer varying capabilities, including flight time, camera quality, and advanced features. Consider your specific needs and budget when selecting a drone.
Operating a drone successfully combines technical skill with responsible decision-making. By following the pre-flight checklists, understanding the controls, and adhering to legal regulations, you can unlock the potential of aerial technology. Remember, continuous practice and a commitment to safety are crucial for honing your skills and ensuring enjoyable and productive drone flights. Embrace the learning process, and soon you’ll be capturing stunning aerial perspectives and navigating the skies with confidence.
FAQ Compilation
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with beginner modes are available. Look for features like GPS stabilization, automatic return-to-home, and intuitive controls.
How long does a drone battery last?
Battery life varies greatly depending on the drone model and flight conditions. Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
What happens if I lose signal with my drone?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that automatically guides the drone back to its starting point if signal is lost. However, always fly within visual line of sight.
Can I fly my drone anywhere?
No. Drone operation is subject to various regulations and restrictions. Check local laws and airspace restrictions before flying.
